Business Models in the Food Delivery Industry: Convenience Meets Innovation
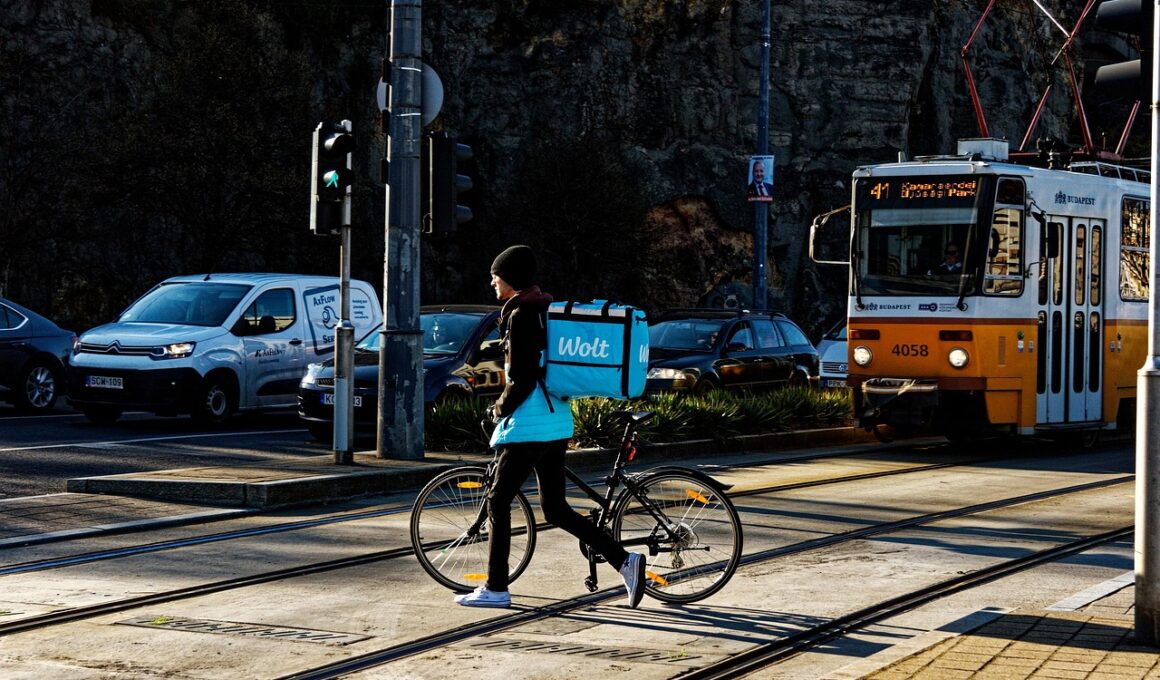
The food delivery industry has undergone remarkable changes in recent years, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. Traditional models focused primarily on restaurant-based delivery strategies. These initial innovations paved the way for robust, technology-driven platforms that drastically shifted customer expectations and industry paradigms. Nowadays, companies leverage mobile applications, algorithmic routing, and delivery partnerships to optimize operations. Enhancing convenience using these technologies significantly appeals to customers who desire instant gratification and simplicity in ordering food. As industries strive to cater to these consumer demands, marketplace dynamics necessitate innovative approaches to stay competitive. The result is a burgeoning landscape characterized by diverse business models that all emphasize enhanced customer experience. Some methods focus on direct-to-consumer methodologies while others rely on extensive partnerships with local restaurants. This unprecedented flexibility gives consumers a vast array of dining options at their fingertips, instantly delivered to their homes. Through this evolution, the food delivery industry showcases the broader implications of integrating technology into traditional sectors, emphasizing innovation’s central role in crafting powerful business models.
One of the most noteworthy transformations within this sector is the rise of meal kit delivery services. These services offer unique propositions that differentiate them from typical food delivery platforms, providing pre-portioned ingredients and curated recipes. Companies harness a subscription model that drives recurring revenue while enhancing customer loyalty. This innovation appealed to consumers interested in cooking at home without the hassle of grocery shopping. Companies like Blue Apron and HelloFresh have found tremendous success as they cater to health-conscious customers seeking fresh ingredients while reducing food waste. Additionally, such services provide an educational component, teaching customers culinary skills and achieving a sense of accomplishment after preparing a meal. Moreover, meal kit services adapt their offerings to seasonal trends and dietary preferences, ensuring variety and personalization. As the market further embraces these innovative models, competition is likely to intensify. This encourages continuous enhancement of service delivery and product offerings. As meal kits and similar innovations continue to gain traction, they underscore the need for continuous adaptation in consumer preferences, not only in food preparation but also concerning overall dining experiences.
Ghost Kitchens: Transforming Delivery Efficiency
Another significant development within the food delivery landscape is the emergence of ghost kitchens or dark kitchens. These kitchens operate without a dine-in facility, solely focusing on fulfilling online orders through food delivery apps. The concept minimizes operational costs while allowing businesses to scale rapidly. Brands can experiment with various culinary concepts without investing in traditional restaurant setups, thereby enhancing overall efficiency. By raising the bar on customer experiences, ghost kitchens are designed to meet growing consumer demand while optimizing the supply chain through centralized production facilities. This model effortlessly addresses the increased consumer appetite for convenience and swift service. Additionally, these kitchens can serve multiple brands from one location, effectively maximizing delivery potential. As labor costs rise, this approach proves to be a sustainable solution, alleviating pressures on restaurant owners while streamlining the ordering and delivery process. With technological innovations bolstering logistics management, ghost kitchens continue to shine amid challenges faced by traditional restaurants. Overall, this business model casts a spotlight on the importance of operational efficiency and adaptability in meeting ever-evolving consumer expectations in the food delivery industry.
Furthermore, partnerships and collaborations within the industry are reshaping the traditional frameworks established by initial delivery models. Food delivery platforms are forming alliances with local restaurants to expand their offerings and infrastructure without bearing the full costs of service expansion. This innovative approach allows smaller businesses to leverage the reach of well-established delivery platforms, enhancing their visibility while tapping into an existing customer base. Conversely, partnering restaurants can benefit from the seamless integration of their menu offerings and dining experiences. Brands like Uber Eats and DoorDash effectively illustrate this collaborative spirit by consistently enhancing their reach through local partnerships. The food delivery industry, therefore, harmonizes the goals of restaurants and delivery services, emphasizing mutual growth. Additionally, such partnerships enable restaurants to gather valuable customer data, helping refine menu offerings and marketing strategies. As businesses develop these business models further, they’ll rely on data analytics to proactively meet consumer demands. This trend promotes innovation as a response to changing consumer behaviors and expectations, reinforcing the importance of collaboration in strengthening the food delivery ecosystem.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
In recent years, sustainability has emerged as a pressing concern for consumers and businesses alike, including those in food delivery. People are more inclined to support brands that prioritize eco-friendly practices, helping foster a reputation aligned with their values. Consequently, many companies are now incorporating sustainable strategies within their operational models, intending to minimize their environmental impact. This shift involves reducing packaging waste, sourcing local ingredients, and employing energy-efficient delivery processes. Establishing transparency about sourcing practices has also resonated well with socially conscious consumers. Moreover, companies that promote their commitment to sustainability often see increased customer loyalty, with consumers willing to pay a premium for environmentally responsible options. By integrating sustainability into their business models, food delivery services create shared value for both customers and the environment. The push for sustainability presents both challenges and opportunities across the supply chain; thus, continual collaborative efforts amongst stakeholders become essential. The growing emphasis on ethical standards amplifies the urgency for food delivery companies to navigate this evolving landscape while ensuring compliance with both consumer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Moreover, technological innovations are integral to transforming the food delivery industry. Automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics pave the way for smarter and more efficient operations. AI-driven algorithms allow businesses to predict consumer preferences and optimize delivery routes, reducing wait times and enhancing customer satisfaction. Additionally, incorporating chatbots and virtual assistants streamlines the ordering process while ensuring effective customer communication. This technological infusion continuously shapes customer experiences, creating a fusion of convenience and accessibility. Furthermore, data-driven insights enable companies to refine their marketing strategies and tailor services according to customer feedback. Adopting such technologies invariably positions businesses to differentiate themselves in an increasingly competitive landscape while remaining responsive to market dynamics. When food delivery companies stay ahead of technological advancements, they can enhance operational efficiency while ensuring that the customer experience remains at the forefront. As technology persists in reshaping the landscape, the subsequent focus lies in harnessing innovative solutions to redefine how consumers access food, providing a unique opportunity for firms embracing digital transformation.
Conclusion: The Future of Food Delivery
In conclusion, the food delivery industry is poised for continued innovation and growth. With diverse business models emerging, companies are constantly adapting to dynamic customer needs, establishing a flexible marketplace. As consumer preferences evolve, brands that successfully blend convenience, sustainability, and technology will likely thrive. Successful business strategies will hinge on leveraging partnerships, refining operational efficiencies, and maintaining a strong focus on customer satisfaction. The industry’s future promises more advancements aimed at enhancing user experiences, particularly in scalability through digital platforms. Thus, as competition intensifies, the need for ongoing innovation remains paramount. With players embracing their creative destinies, food delivery will likely become an indispensable part of our modern dining ecosystem. Companies that forgo complacency, choosing instead to pioneer alternative approaches to traditional business models, will undoubtedly lead the charge in transforming food delivery into a more accessible, delicious, and environmentally conscious service for all consumers.